티스토리 뷰
springboot에 대해 이론적으로 열심히 공부를 해보지는 않았지만 사용해보면서 기존 spring과 가장 많이 다르다고 느낀점은 크게 두가지가 있다. 하나는 embedded was를 사용하여 간단히 구동을 시켜볼 수 있다(Stand-Alone application)는 점이 있고 두번째는 어플리케이션 구성의 간소화이다. 바로 이 구성의 간소화를 하는데 있어서 많은 역할을 해주는것이 바로 이 spring-boot-starter이다. 이게 무슨 역할을 해주는지 한번 보자.
기존에 우리가 spring batch를 사용하기 위해서는 다음과 같은 dependency를 pom.xml 에 추가를 해줘야 했다.
AS-IS spring framework pom.xml
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>5.1.4.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.1.4.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.batch</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-batch-core</artifactId>
<version>4.1.1.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<!--jdbc-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.1.4.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.zaxxer</groupId>
<artifactId>HikariCP</artifactId>
<version>3.2.0</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<!--logging-->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-to-slf4j</artifactId>
<version>2.11.1</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>jul-to-slf4j</artifactId>
<version>1.7.25</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.annotation</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.annotation-api</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
...이건 일부일 뿐이고 실제로 구현을 하다보면 더 많은 부분이 추가가 되어야 한다. 이 부분이 spring이 어렵다고 느끼게 되는 부분이다. 왜냐면 내가 필요로 하는 기능이 어떤 dependency를 필요로 하고 이는 다른 dependency와 어떤 관계가 있는지, dependency의 version은 어떤걸 써야 하는지 등등 하나하나 다 찾아서 세팅을 해야 하기 때문이다. 누군가가 만들어 놓은 개발환경을 받아서 사용하는 입장이라면 잘 모를수도 있지만 이를 다 구성해야 하는 입장에서는 상당히 골치아픈 일이 아닐수 없다. 이런 구성을 간편하게 해주는 역할을 하는것이 spring-boot-starter 이다. 이를 활용하면 굉장히 간단하게 spring framework를 구성할 수 있어 초기 세팅 시간이 비약적으로 줄어든다. 따라서 이런 개발환경 구성에 쏟는 시간을 줄이고 개발에 집중할 수 있도록 해준다.
spring-boot-starter를 사용하여 프로젝트 구성을 하는것을 한번 살펴보자.
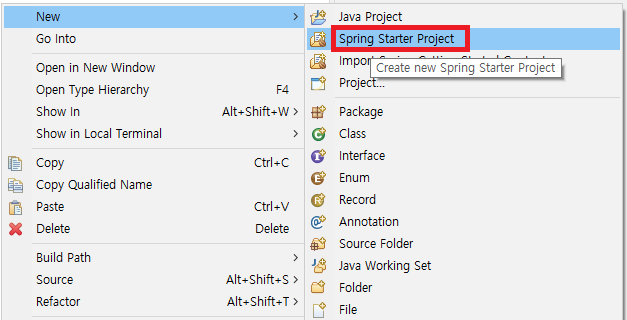
이클립스에서 새로운 프로젝트를 만들 때 Spring Starter Project로 생성을 한다.

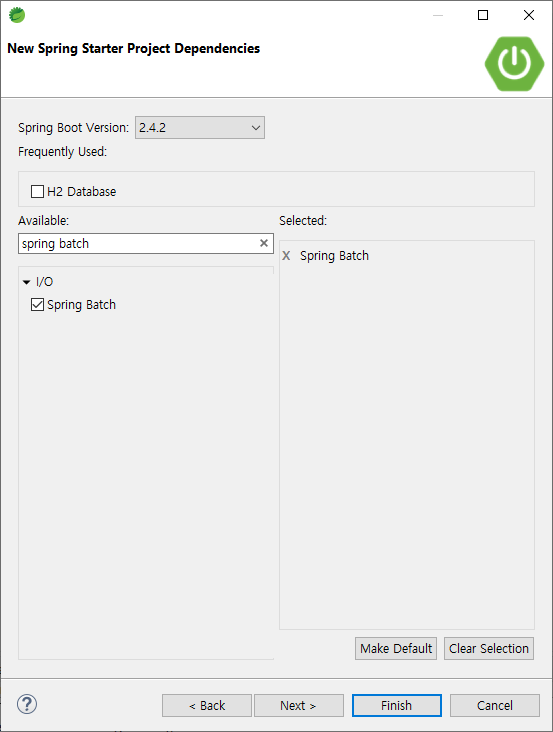
project의 기본 정보를 넣고 spring batch 프로젝트를 사용한다고 선택을 하면 spring batch를 사용할 수 있는 준비가 끝이 난다. 기존에 pom.xml 에 spring batch를 할때 필요한 denpendency를 퍼즐하듯 짜맞추던 고생은 더이상 할 필요가 없다.
springboot framework pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-batch</artifactId>
</dependency>
이렇게 생성된 프로젝트의 pom.xml 의 모습은 위와 같다. 딱 저것만 존재한다.
예전의 spring dependency 설정을 자유여행 이라고 한다면 spring-boot-starter를 이용한 설정은 패키지여행과 같다고 보면 된다. 내가 갈 목적지에 대한 설정만 한다면 나머지는 다 spring-boot-starter가 알아서 해준다.
이런 목적지에 해당하는 것들은 다음과 같다.
spring-boot-starter 의 종류
|
startersName |
Description |
|
spring-boot-starter |
Core starter, including auto-configuration support, logging and YAML |
|
spring-boot-starter-activemq |
Starter for JMS messaging using Apache ActiveMQ |
|
spring-boot-starter-amqp |
Starter for using Spring AMQP and Rabbit MQ |
|
spring-boot-starter-aop |
Starter for aspect-oriented programming with Spring AOP and AspectJ |
|
spring-boot-starter-artemis |
Starter for JMS messaging using Apache Artemis |
|
spring-boot-starter-batch |
Starter for using Spring Batch |
|
spring-boot-starter-cache |
Starter for using Spring Framework’s caching support |
|
spring-boot-starter-data-cassandra |
Starter for using Cassandra distributed database and Spring Data Cassandra |
|
spring-boot-starter-data-cassandra-reactive |
Starter for using Cassandra distributed database and Spring Data Cassandra Reactive |
|
spring-boot-starter-data-couchbase |
Starter for using Couchbase document-oriented database and Spring Data Couchbase |
|
spring-boot-starter-data-couchbase-reactive |
Starter for using Couchbase document-oriented database and Spring Data Couchbase Reactive |
|
spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch |
Starter for using Elasticsearch search and analytics engine and Spring Data Elasticsearch |
|
spring-boot-starter-data-jdbc |
Starter for using Spring Data JDBC |
|
spring-boot-starter-data-jpa |
Starter for using Spring Data JPA with Hibernate |
|
spring-boot-starter-data-ldap |
Starter for using Spring Data LDAP |
|
spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb |
Starter for using MongoDB document-oriented database and Spring Data MongoDB |
|
spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb-reactive |
Starter for using MongoDB document-oriented database and Spring Data MongoDB Reactive |
|
spring-boot-starter-data-neo4j |
Starter for using Neo4j graph database and Spring Data Neo4j |
|
spring-boot-starter-data-r2dbc |
Starter for using Spring Data R2DBC |
|
spring-boot-starter-data-redis |
Starter for using Redis key-value data store with Spring Data Redis and the Lettuce client |
|
spring-boot-starter-data-redis-reactive |
Starter for using Redis key-value data store with Spring Data Redis reactive and the Lettuce client |
|
spring-boot-starter-data-rest |
Starter for exposing Spring Data repositories over REST using Spring Data REST |
|
spring-boot-starter-data-solr |
Starter for using the Apache Solr search platform with Spring Data Solr |
|
spring-boot-starter-freemarker |
Starter for building MVC web applications using FreeMarker views |
|
spring-boot-starter-groovy-templates |
Starter for building MVC web applications using Groovy Templates views |
|
spring-boot-starter-hateoas |
Starter for building hypermedia-based RESTful web application with Spring MVC and Spring HATEOAS |
|
spring-boot-starter-integration |
Starter for using Spring Integration |
|
spring-boot-starter-jdbc |
Starter for using JDBC with the HikariCP connection pool |
|
spring-boot-starter-jersey |
Starter for building RESTful web applications using JAX-RS and Jersey. An alternative to spring-boot-starter-web |
|
spring-boot-starter-jooq |
Starter for using jOOQ to access SQL databases. An alternative to spring-boot-starter-data-jpa or spring-boot-starter-jdbc |
|
spring-boot-starter-json |
Starter for reading and writing json |
|
spring-boot-starter-jta-atomikos |
Starter for JTA transactions using Atomikos |
|
spring-boot-starter-jta-bitronix |
Starter for JTA transactions using Bitronix. Deprecated since 2.3.0 |
|
spring-boot-starter-mail |
Starter for using Java Mail and Spring Framework’s email sending support |
|
spring-boot-starter-mustache |
Starter for building web applications using Mustache views |
|
spring-boot-starter-oauth2-client |
Starter for using Spring Security’s OAuth2/OpenID Connect client features |
|
spring-boot-starter-oauth2-resource-server |
Starter for using Spring Security’s OAuth2 resource server features |
|
spring-boot-starter-quartz |
Starter for using the Quartz scheduler |
|
spring-boot-starter-rsocket |
Starter for building RSocket clients and servers |
|
spring-boot-starter-security |
Starter for using Spring Security |
|
spring-boot-starter-test |
Starter for testing Spring Boot applications with libraries including JUnit Jupiter, Hamcrest and Mockito |
|
spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf |
Starter for building MVC web applications using Thymeleaf views |
|
spring-boot-starter-validation |
Starter for using Java Bean Validation with Hibernate Validator |
|
spring-boot-starter-web |
Starter for building web, including RESTful, applications using Spring MVC. Uses Tomcat as the default embedded container |
|
spring-boot-starter-web-services |
Starter for using Spring Web Services |
|
spring-boot-starter-webflux |
Starter for building WebFlux applications using Spring Framework’s Reactive Web support |
|
spring-boot-starter-websocket |
Starter for building WebSocket applications using Spring Framework’s WebSocket support |
참고 : docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/htmlsingle/#using-boot-starter
내가 하고자 하는 프로젝트의 성격에 맞게 위의 starter에서 선택을 해주면 된다. 세상 많이 좋아졌다.
그럼 spring-boot-starter-parent 는 무슨 역할을 할까?
위와 같이 Spring Starter Project로 프로젝트를 생성을 하면 맨 위에 spring-boot-starter-parent가 추가되어 있다.
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.4.2</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>starter가 dependency의 조합을 해준다면 parent는 dependency의 버전정보에 대한 관리를 해준다. 실제로 일일히 dependency 설정을 하면 각 라이브러리마다 버전이 맞지 않아서 오류가 많이 발생하는데 parent를 사용하면 각 dependency의 버전을 알아서 맞춰줘서 버전충돌 이슈로부터 자유로워질수 있다. 또한 위의 starter를 설정한 pom.xml 을 보면 버전정보가 없는데 이 parent에서 관리를 해주기 때문이다.
요약하자면, spring에 대해 잘 모르는 사람이라도 쉽게 spring에 접근해서 개발할 수 있도록 spring-boot-starter, parent 가 springboot framework에서 추가가 되었고 우리는 쉽게 개발환경을 구성할 수 있게 되었다.
끝!
'Framework > Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Springboot에서 API Docs (Springdoc) 사용하는 방법 (2) (2) | 2021.02.19 |
|---|---|
| Springboot에서 API Docs (Springdoc) 사용하는 방법 (1) (0) | 2021.02.18 |
| Spring Validation Message properties 파일을 통해 관리하기 (2) | 2021.02.09 |
| Spring에서 h2 database 간단 사용법 (1) | 2021.02.03 |
| Springboot 에서 @ComponentScan 설정 및 사용법 (2) | 2021.01.14 |
